여러테이블을 조인하는 실습을 해보겠습니다.
1. 테이블 생성
- customers (고객정보)
- orders (주문정보)
- products (제품정보)
- order_items (주문항목 정보)
test9 데이터베이스 안에 위 4개에 테이블을 생성해줬습니다.
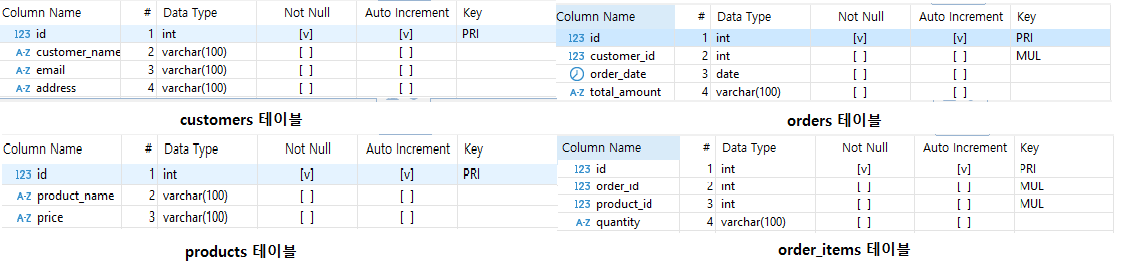
2. Foreign Keys 설정
위 사진에서 MUL이라고 표시되어있는 부분이 foreign key가 설정되어있음을 알 수 있습니다.
orders테이블과 orders_items 테이블에 id가 아닌 customer_id, order_id, product_id 컬럼이 있죠?
foreign key 설정을 할 때 이 컬럼들을 선택하면 됩니다.
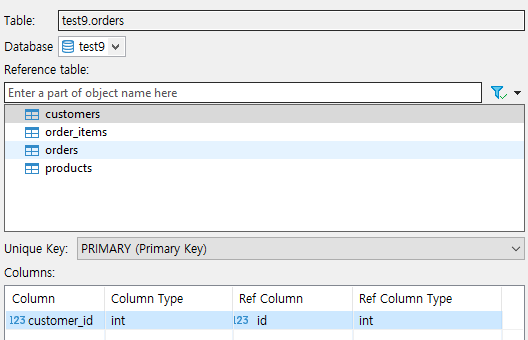
- orders 테이블에서 customers 테이블과 연결
- order_items 테이블에서 orders, products 연결
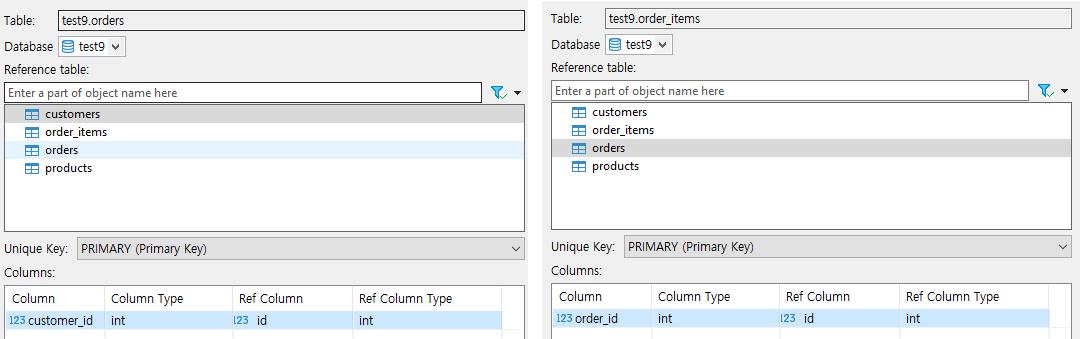
이제 test9 를 더블클릭해서 ER Diagram을 클릭하면 Foreign Key가 설정되어있는 걸 확인할 수 있습니다.

3. 데이터 추가
-- customers table data
INSERT INTO customers (customer_name, email, address) VALUES
('김철수', 'kimchulsoo@example.com', '서울시 강남구'),
('이영희', 'leeyounghee@example.com', '서울시 마포구'),
('박준혁', 'parkjunhyuk@example.com', '경기도 수원시'),
('최수진', 'choisujin@example.com', '부산시 해운대구'),
('정우진', 'jungwoojin@example.com', '대구시 수성구'),
('한지수', 'hanjisu@example.com', '서울시 성동구'),
('김지훈', 'kimjihun@example.com', '인천시 남동구'),
('이민영', 'leeminyoung@example.com', '경기도 고양시'),
('장서현', 'jangseohyun@example.com', '서울시 종로구'),
('박다연', 'parkdayeon@example.com', '전라북도 전주시'),
('윤성민', 'yoonseongmin@example.com', '강원도 원주시'),
('신예린', 'shinyeorin@example.com', '서울시 관악구'),
('오지훈', 'ohjihoon@example.com', '서울시 구로구'),
('김서준', 'kimseojun@example.com', '경기도 파주시'),
('이하은', 'leehaneun@example.com', '서울시 동작구'),
('문찬영', 'moonchanyeong@example.com', '경기도 용인시'),
('임수연', 'imsuyeon@example.com', '울산시 남구'),
('유진우', 'yoojinu@example.com', '서울시 서초구'),
('정하영', 'jeonghayoung@example.com', '경기도 성남시'),
('최민준', 'choiminjun@example.com', '서울시 송파구');
-- orders table data (reflecting multiple purchases by some users and no purchases by others)
INSERT INTO orders (customer_id, order_date, total_amount) VALUES
(1, '2023-10-01', 2500000),
(2, '2023-10-03', 1800000),
(1, '2023-10-10', 2200000),
(3, '2023-10-12', 3000000),
(4, '2023-10-15', 800000),
(2, '2023-10-18', 1400000),
(5, '2023-10-20', 1800000),
(6, '2023-10-25', 1600000),
(1, '2023-10-27', 1900000),
(3, '2023-10-29', 2000000),
(7, '2023-11-01', 2200000),
(8, '2023-11-05', 2500000),
(9, '2023-11-08', 800000),
(10, '2023-11-11', 1300000),
(2, '2023-11-15', 1500000),
(4, '2023-11-20', 1700000),
(11, '2023-11-22', 2000000),
(12, '2023-11-25', 2100000),
(6, '2023-11-28', 1800000),
(8, '2023-11-30', 1600000);
-- products table data
INSERT INTO products (product_name, price) VALUES
('노트북', 1200000),
('스마트폰', 800000),
('태블릿', 600000),
('헤드폰', 200000),
('이어폰', 100000),
('스마트워치', 300000),
('모니터', 700000),
('마우스', 50000),
('키보드', 80000),
('USB 메모리', 20000),
('외장하드', 100000),
('파워뱅크', 150000),
('충전기', 40000),
('케이블', 10000),
('프린터', 500000),
('책상', 100000),
('의자', 200000),
('모니터 받침대', 50000),
('스피커', 300000),
('마이크', 60000);
-- order_items table data (reflecting multiple items per order)
INSERT INTO order_items (order_id, product_id, quantity) VALUES
(1, 1, 1),
(1, 2, 2),
(2, 3, 1),
(2, 4, 3),
(3, 5, 2),
(3, 1, 1),
(4, 6, 2),
(5, 7, 1),
(5, 3, 1),
(6, 8, 2),
(7, 9, 4),
(8, 10, 1),
(9, 1, 1),
(9, 6, 1),
(10, 2, 2),
(10, 5, 1),
(11, 3, 3),
(12, 4, 1),
(13, 5, 1),
(14, 8, 2),
(15, 1, 2),
(15, 5, 1),
(16, 2, 3),
(16, 3, 1),
(17, 4, 2),
(17, 6, 1),
(18, 7, 1),
(18, 8, 4),
(19, 9, 2),
(20, 3, 2),
(20, 5, 3);
4. 실습문제
1. 고객 이름과 주문날짜를 조회하세요.
select c.customer_name, o.order_date
from orders o
left join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id;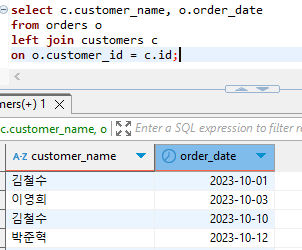
2. 각 주문에 대해 주문번호, 고객 이름, 주문 총액을 조회하세요.
select o.id, c.customer_name, o.total_amount
from orders o
left join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id
group by o.id;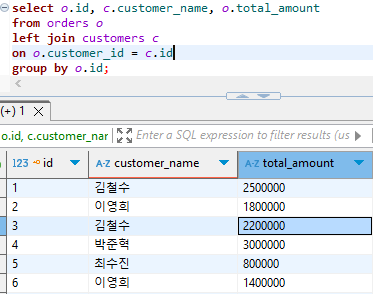
3. 제품 이름과 가격을 조회하세요.
select product_name, price
from products;
4. 주문한 고객의 이름과 해당 주문에서 구매한 제품의 이름을 조회하세요.
select c.customer_name, p.product_name
from order_items oi
left join products p
on oi.product_id = p.id
join orders o
on oi.order_id = o.id
join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id;
5. 주문 id 15에 포함된 제품 이름과 수량을 조회하세요.
select p.product_name, oi.quantity
from order_items oi
left join products p
on oi.product_id = p.id
where order_id = 15;
6. 총액(total_amount)이 200만원 이상인 주문의 데이터를 가져와서, 고객 이름과 주문 총액(total_amount)을 조회하세요.
select c.customer_name, o.total_amount
from orders o
left join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id
where total_amount >= 2000000;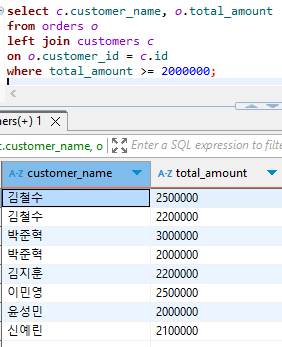
7. 모든 주문에 대해 고객의 이름과 해당 고객이 주문한 제품 수량을 조회하세요.
select c.customer_name, oi.quantity
from order_items oi
left join products p
on oi.product_id = p.id
join orders o
on oi.order_id = o.id
join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id;
8. 각 주문에 포함된 총 제품 수량을 조회하세요.
select order_id, sum(quantity) quantity
from order_items
group by order_id;
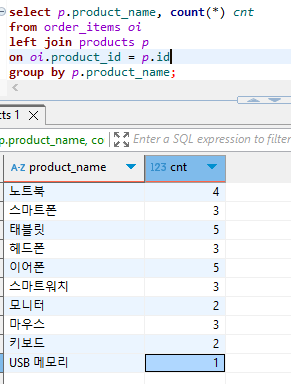
9. 제품 이름과, 해당 제품이 포함된 주문의 총 주문횟수를 조회하세요.
select p.product_name, count(*) cnt
from order_items oi
left join products p
on oi.product_id = p.id
group by p.product_name;
10. 2023년 10월에 주문한 고객의 이름과 주문 총액을 조회하세요.
select c.customer_name, sum(o.total_amount) total_amount
from orders o
left join customers c
on o.customer_id = c.id
where order_date like '2023-10%'
group by c.id;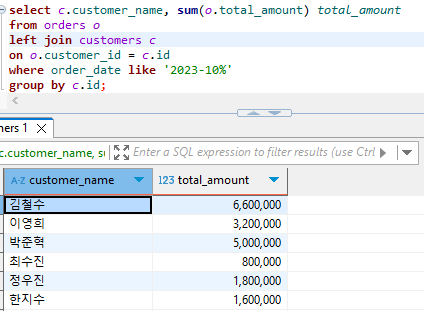
'Database > MySQL 실습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [DBeaver-MySQL] : (스키마 설계) 영화 리뷰 서비스 개발 실습 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
|---|---|
| [DBeaver] MySQL 실습 - 시간처리 실습 (2) | 2025.02.02 |
| [DBeaver] MySQL 실습 - 키워드를 이용해 특수한 컬럼 조회하기 : group by, having (0) | 2025.01.28 |
| [DBeaver] MySQL 실습 - CRUD 및 문자열 처리 실습 2 (0) | 2025.01.14 |
| [DBeaver] MySQL 실습 - CRUD 및 문자열 처리 실습 (0) | 2025.01.12 |


